RTOS Security Designed in Accordance with ISO 21434 for Safety-Critical Embedded Systems
The Enhanced Security Module (ESM) is a cybersecurity extension for SAFERTOS®, a real-time operating system used in safety-critical embedded systems. The ESM is purpose-built to protect automotive and industrial applications by isolating tasks, detecting threats, and preventing unauthorized access to system resources. It is designed in accordance with ISO 21434, the global standard for road vehicle cybersecurity. By enforcing strict access controls and memory isolation, the ESM helps developers meet functional safety and cybersecurity goals in modern embedded environments.

Ask Us a Question
For pricing, licensing, or any other sales or product related questions, please contact us.

Table Top Talks
Want to hear more about the SAFERTOS® Enhanced Security Module? Watch our table top talk from Embedded World 2025 to discover how this innovative solution fortifies your devices against cyber threats, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring unparalleled protection.
This video introduces the SAFERTOS® Enhanced Security Module (ESM) and its role in strengthening embedded cybersecurity. It highlights how ESM is designed in accordance with ISO 21434, the automotive cybersecurity standard, and explains how it enhances the security of real-time operating systems.
Miss out on our other table top talks? You can watch them here.
Security features that protect your embedded system
- Access Control Policy (ACP) – Restricts API access per Task
- Object Control Policy (OCP) – Limits access to RTOS objects
- Data Obfuscation – Hides critical structures via indirect references
- Memory Isolation – Defines MPU/MMU regions per Task
- Secure Portable Layer – Enforces kernel/user space separation
- Task Context Data Isolation – Stores context in TCB, not stack
- Penetration Detection Monitor – Triggers alerts on unauthorized access
For more information on these features, visit our Download Centre to get a copy of the ESM technical Datasheet.
How SAFERTOS® ESM Is Built for Safety and Cybersecurity
SAFERTOS® ESM is developed using the same rigorous lifecycle as SAFERTOS®, which is certified to ISO 26262 and IEC 61508, among others. To meet the growing demands of embedded cybersecurity—especially in automotive applications—the ESM development process includes additional steps that focus specifically on identifying and mitigating security risks.
These additions ensure that cybersecurity is considered from the earliest stages of development, alongside functional safety.
Key Additions to the Development Lifecycle:
- Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA):
Identifies potential cybersecurity threats and evaluates their impact and likelihood. - Cybersecurity Analysis Report (CAR):
Documents security requirements and how they are addressed throughout development. - Penetration Testing:
Simulates attacks to uncover vulnerabilities in the system. - Fuzz Testing:
Sends unexpected or random inputs to the system to test its resilience against malformed data. - Integrated Safety and Security Requirements:
All safety, functional, and security requirements are managed together to ensure consistency and traceability.
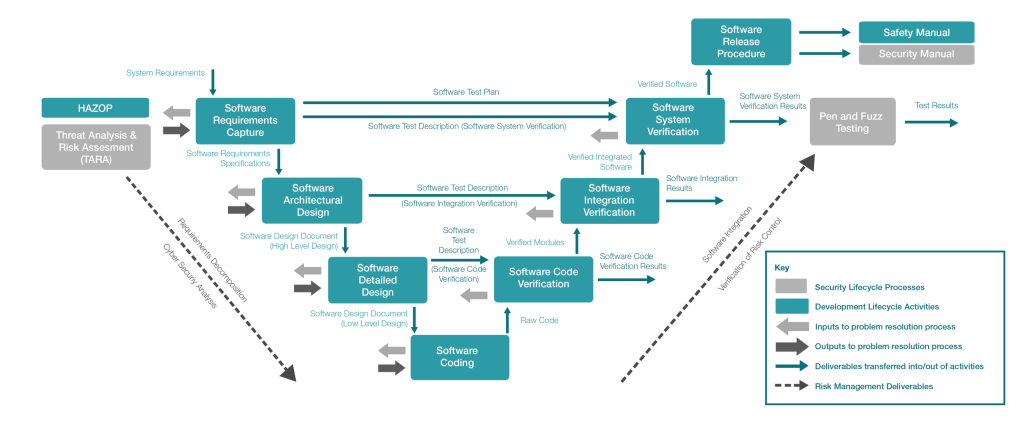
These activities are layered on top of traditional safety processes such as HAZOP, requirements capture, and system verification, resulting in a development lifecycle that supports both functional safety and cybersecurity assurance.
Related Blogs on Embedded Cybersecurity and ISO 21434
Stay informed with expert insights on embedded system security, functional safety, and ISO 21434 alignment. These blog articles explore real-world challenges and solutions for securing safety-critical applications in automotive and industrial environments.
🔹 Safety vs. Security: Understanding the Differences
Clarifies how functional safety and cybersecurity intersect in embedded systems, and why both are essential for modern product development.
🔹 Securing Embedded Devices: A Multi-Layered Approach
Outlines how SAFERTOS® and the Enhanced Security Module work together to protect against evolving cyber threats.
🔹 Performing the TARA Analysis
Explains how Threat Analysis and Risk Assessment (TARA) is applied in line with ISO 21434 to identify and mitigate risks in automotive software.



